What is a software factory, what is its value contribution and why hire one?
Like a traditional industrial factory, a software factory focuses on product development, although instead of creating physical goods, it generates IT solutions.
In this article we analyze the essential components of a software factory, how its development processes are organized and what added value they bring to the production system.
What are the dimensions of the software industry globally?
A report by 360 Research Reports provides that the global software market will increase at a considerable pace between 2023 and 2030, at a CAGR of +8,46%.
In terms of money, after being valued at $60,938.08 million in 2021, the expectation is that will expand to reach 99,226.01 million dollars in 2027.
For its part, Global Market Insights estimates an annual growth rate of 21.5% between 2023 and 2032.
As can be seen from these trends, in either case a person is being portrayed industry in full growth.
Essential components of a software factory
Achieving efficient, high-quality software product development requires components that vary by organization, development team preferences, and project needs.
However, all projects share the following common components and professional roles involved.
Development team
Formed by software engineers, designers, business analysts, testers, and other professionals involved in the life cycle of computer products.
Project management
Comprised of project managers, scrum masters, and other roles, who oversee project progress, assign tasks, manage resources, and ensure timely delivery and on budget.
Infrastructure
It covers the technological resources necessary for software development, such as hardware, servers, development tools, version control systems and test environments.
Methodologies and processes
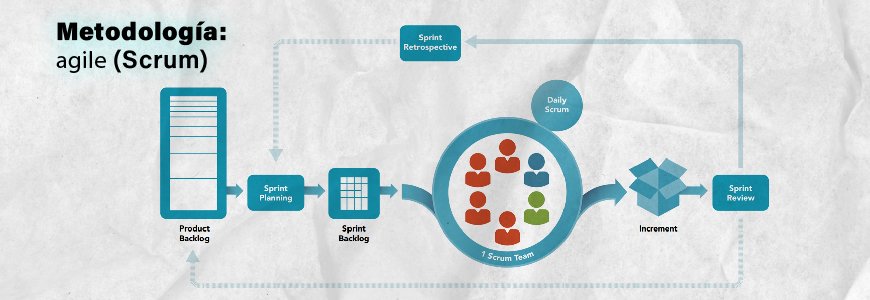
Software factories often adopt specific software development methodologies and practices adapted to the needs of the organization and the project. Later we will expand on why software factories are currently highly valued. Agile methodologies, such as Scrum or Agile.
Collaboration environment
Communication and collaboration platforms are required for work effectively, share information, coordinate activities and stay updated on project progress.
Quality management
Allows ensure the quality of the software developed. For example, unit, integration, user acceptance testing, and code reviews.
Documentation
The right tools and processes to document requirements, specifications, designs, changes, and other aspects of the project. Also for manage and share knowledge within the team.
Support and maintenance
Services for troubleshooting, apply security patches, and perform updates and upgrades to the software after it is implemented.
Configuration management
To control versions, track changes and ensure the consistency and integrity of the source code.
Talent management
Activities related to recruitment, training, professional development, motivation and retention of talent.

Development methodologies most implemented by a software factory
As we mentioned before, software factories usually follow methodologies such as Agile, Scrum or DevOps. Why? To promote Managing the life cycle of projects in an efficient and agile manner.
The key is to keep in mind that methodologies can vary depending on the context and specific needs of each company, each client and each project.
Among the most popular are:
1) Agile Methodologies
Scrum, Kanban, Extreme Programming (XP) and Lean Development are among the most popular. Their main characteristics are the focus on incremental value delivery, constant collaboration with the client and the ability to respond to changes.
2) Iterative and incremental development
This philosophy is based on short development cycles (iterations), where parts of the software are built and improved incrementally. This allows for early feedback and more effective adaptation to changes.
3) DevOps
The expression refers to the culture and set of practices that integrates software development (Dev) with IT operations (Ops).
It includes process automation, collaboration between development and operational teams, and continuous deployment to achieve faster and more reliable life cycles.
4) Lean and Six Sigma
Both approaches focus on eliminating waste and continuously improving processes. In a software factory, they can be applied to optimize workflows, reduce delivery times, and improve the quality of the final product.
The key word to keep in mind at this point is “optimization.”
6) Project management and quality
They apply project management and software quality practices and standards. For example, the Capability Maturity Model (CMMI), and the ISO 9001 and ISO 27001 standards, among others.
What type of products does a software factory typically develop?
A software factory can develop a wide variety of IT products, with the aim of satisfying the needs of different clients.
Some examples are:
- Web and mobile applications for various platforms and devices.
- Enterprise resource planning systems for managing complex business processes. For example: finance, HR, insurance, inventory and logistics.
- CRM systems for managing customer relationships, which include functions such as sales management, marketing, customer service and data analytics.
- CMS platforms for creating, managing and publishing online content.
- Tools for planning, tracking and collaborating on projects, including task management, calendars and communication.
- Industrial automation systems for process monitoring, quality control, and real-time data monitoring and analysis.
- Software for embedded devices, such as vehicle control systems, medical devices and smart home appliances.
- Solutions based on artificial intelligence, machine learning and data analysis, to provide insights, automate processes and make smart decisions.
- Solutions to protect information, such as intrusion detection systems, firewalls, antivirus software and encryption tools.
Why should I hire a software factory?
Hiring a software factory is beneficial for organizations looking to develop IT platforms and tools in a efficient, cost-effective, with high quality and high levels of safety.
In addition to facilitating the organization and management of teams and processes, it allows companies to maintain focus on their business, while taking advantage of the specialization and experience of external suppliers.
Among the main reasons why it is convenient to hire the services of a software factory are:
1) Cost reduction
Hiring a software factory is, in general, more economically convenient to form and maintain an internal software development team.
In this way, companies avoid high fixed costs related to hiring, training and staff management.
2) Flexibility and scalability
Software factories easily adapt to changing project needs and can offer additional resources as needed.
This allows Quickly scale or down a development team, according to each project, without compromising its quality or efficiency.
3) Time saving
Software factories are equipped with optimized tools and processes that can accelerate software development.
This allows for faster technological solutions and the resolution of business needs or the taking advantage of market opportunities in a more agile manner.
4) Specialization and experience
They have teams of highly specialized and experienced professionals in software development. They have up-to-date technical knowledge and have experience in a variety of technologies and development methodologies.
This ensures quality and efficiency in project delivery.
5) Focus on the client's core business
By outsourcing software development, companies can focus on its core and strategic activities.
6) Access to advanced technologies
Software factories keep up with the latest trends and technological advancements in the field of IT development. This allows contracting organizations to access advanced and innovative solutions, which improve the competitiveness and efficiency of their operations.
Conclusion: What is the added value that a software factory provides?
Software factories that specialize in specific sectors of the economy have the experience, knowledge and best practices in developing specific technological solutions, in accordance with the business rules of that specific activity.
In addition, they understand the challenges, regulations and standards specific to each industry, allowing them to offer tailored solutions focused on the needs of each sector.
Finally, they have senior development cells, which ensure the skills and experience necessary to meet project objectives.
Are you interested in learning more about the added value that our Software Studio can bring to your company? Contact us and we'll talk.

